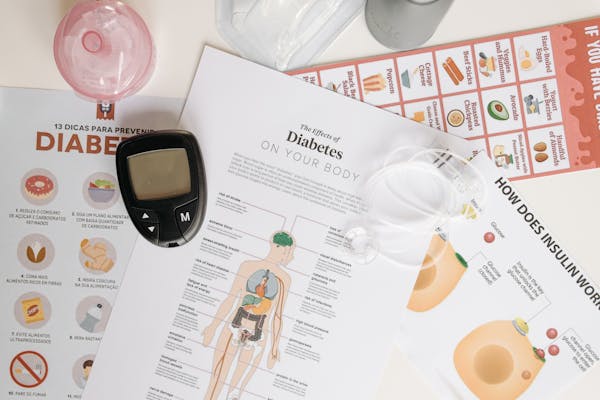
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Its prevalence continues to rise, making it a significant public health concern. The two primary types of diabetes, Type 1 and Type 2, have distinct causes and treatment strategies. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of diabetes prevention and treatment, highlighting lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and ongoing research.
Understanding Diabetes
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period. It occurs when the body cannot effectively use or produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar.
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. It usually manifests in childhood or adolescence.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. It is often associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle and typically develops in adults over 45, though it’s increasingly seen in younger populations.
- Gestational Diabetes: A temporary form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
Several risk factors contribute to the development of diabetes. Understanding these can aid in diabetes prevention and treatment:
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Age: Risk increases with age, particularly for Type 2 diabetes.
- Weight: Obesity is a major risk factor for Type 2 diabetes.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to insulin resistance.
- Diet: Poor dietary habits, including high sugar intake and low fiber consumption, increase risk.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asian Americans, are at higher risk.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Unexplained weight loss (more common in Type 1)
- Frequent infections
Early detection through regular screenings is crucial for effective diabetes prevention and treatment.
Diabetes Prevention and Treatment
Diabetes Prevention Strategies
Preventing diabetes, particularly Type 2, involves lifestyle modifications that can also benefit overall health. Here are some key strategies for diabetes prevention and treatment:
Healthy Eating
A balanced diet is fundamental in preventing diabetes. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Limit Sugar and Refined Carbs: Reducing the intake of sugary drinks, sweets, and refined carbohydrates helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can help regulate blood sugar and promote satiety.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats.
- Portion Control: Managing portion sizes can prevent overeating and help maintain a healthy weight.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise plays a crucial role in diabetes prevention and treatment:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling help improve insulin sensitivity.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass through resistance exercises can enhance glucose uptake.
- Consistency: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most effective ways to prevent Type 2 diabetes. Weight loss, even a modest amount, can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Avoiding Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol
- Tobacco Use: Smoking increases the risk of diabetes and its complications.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can lead to weight gain and increased blood pressure, contributing to diabetes risk.
Medical Interventions for Diabetes Prevention
In addition to lifestyle changes, certain medical interventions can aid in diabetes prevention and treatment:
Medication
- Metformin: Often prescribed to people with prediabetes to prevent the progression of Type 2 diabetes.
- Other Medications: Medications like thiazolidinediones and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors may also be used in high-risk individuals.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels can help identify and manage prediabetes, preventing the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
Bariatric Surgery
For individuals with severe obesity, bariatric surgery may be considered. This procedure has been shown to improve or even resolve Type 2 diabetes in many patients.
Treatment of Diabetes
Effective management of diabetes requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. Here, we explore the components of diabetes treatment.
Lifestyle Modifications
Many of the lifestyle changes used in diabetes prevention are also essential in the treatment of diabetes:
- Diet: Following a balanced diet tailored to individual needs, often with the guidance of a dietitian.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
- Weight Management: Maintaining or achieving a healthy weight is crucial for blood sugar control.
Medications
Several classes of medications are used to manage diabetes:
- Insulin Therapy: Essential for Type 1 diabetes and sometimes used in Type 2 diabetes.
- Oral Medications: Such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors.
- Non-Insulin Injectables: Including GLP-1 receptor agonists and amylin analogs.
Monitoring Blood Glucose
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels helps individuals with diabetes manage their condition effectively. Tools for monitoring include:
- Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose (SMBG): Using a blood glucose meter.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Devices that provide real-time glucose readings.
- HbA1c Testing: A lab test that measures average blood glucose over the past two to three months.
Managing Complications
Diabetes can lead to serious complications if not managed properly. Key areas of focus include:
- Cardiovascular Health: Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Foot Care: Regular foot exams and proper foot care to prevent ulcers and infections.
- Eye Care: Annual eye exams to detect diabetic retinopathy.
- Kidney Health: Monitoring kidney function through regular tests.
Advanced Treatments and Research
Ongoing research continues to explore new treatments and potential cures for diabetes. Some of the promising areas include:
Artificial Pancreas
An artificial pancreas system, combining an insulin pump and a continuous glucose monitor, automatically adjusts insulin delivery based on blood sugar levels. This technology offers improved blood sugar control and reduced burden for people with Type 1 diabetes.
Islet Cell Transplantation
Islet cell transplantation involves transplanting insulin-producing beta cells from a donor into a person with Type 1 diabetes. While still experimental, this approach shows promise in reducing or eliminating the need for insulin injections.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy aims to correct genetic defects causing diabetes. Although still in the early stages, this approach holds potential for long-term treatment or even a cure for certain types of diabetes.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell research is exploring ways to generate new insulin-producing cells to replace damaged ones. This could potentially offer a regenerative treatment for Type 1 diabetes.
Conclusion
Diabetes prevention and treatment require a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and regular monitoring. While Type 1 diabetes currently has no known prevention, Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented through healthy living and early intervention.
The management of diabetes involves a combination of diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring to prevent complications and maintain a high quality of life. Advances in research continue to offer hope for improved treatments and potential cures, making the future brighter for those living with diabetes.
By understanding and implementing the strategies outlined in this article, individuals can take proactive steps toward diabetes prevention and treatment, ultimately leading to healthier and more fulfilling lives.